Market Research
Missions and definitions of marketing research
Customer insights
Customer insights: fresh marketing information-based understandings of customers and the marketplace that become the basis for creating customer value, engagement, and relationships.
Developing marketing information
INTERNATAL DATA: collections of consumer and market information within the company network.
MARKETING INTELLIGENCE: Systematic collection and analysis of publicly available information about consumers, competitors, and developments
Market Research
The systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data relevant to a specific marketing situation facing an organization.
Types of research
Primary data: information collected for the specific purpose at hand (qualitative or quantitative) Secondary data: information done by someone else (Internet, information desk, etc.)
Gathering Secondary Data
-
Advantages
- Lower cost
- Obtained quickly
- Cannot collect otherwise
-
Disadvantages
-
Data may not be:
- Relevant
- Accurate
- Current
- Impartial
-
Objective of Market Research
- Help with comprehension (describe, analyze, measure, anticipate the demand and its influencing factors)
- Help with decision making
- Help with control (analyze performance and results)
Marketing Research Process


Types of research
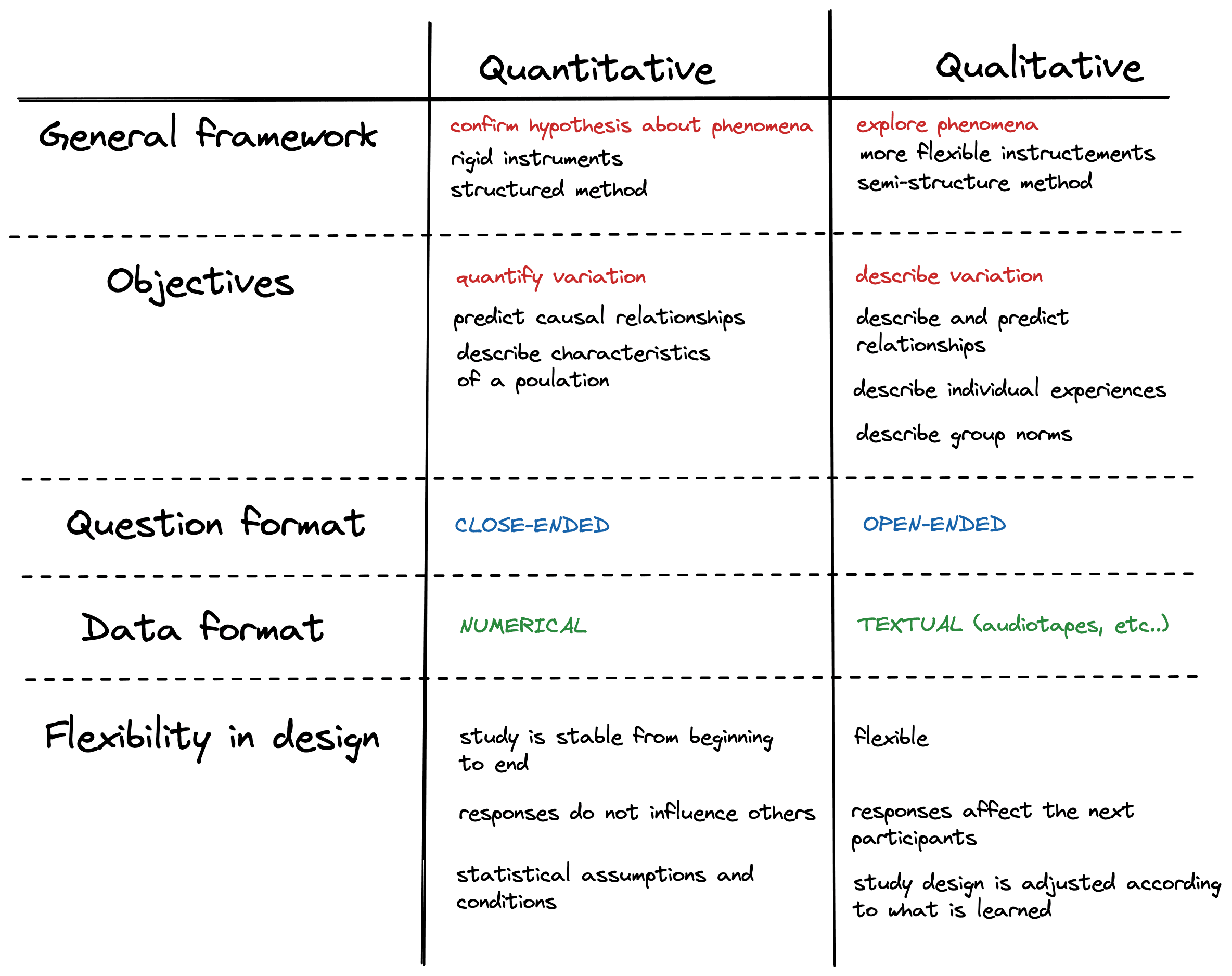
Qualitative Research
- intensive studies using an
open,
non-directive
, permissive, and
indirect approach of respondents to collect data. - collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio)
How does it work ?
- Conducted by a specialist
- Small sample
- Selection mode of participants
- Analysis
What for ?
- Exploratory basis study
- Sensitive matter
- Knowledge enhancement
- Screening/alternative reduction
- New idea generation
Types
- Focus group: small group, open debate, one moderator, interaction between participants, timing, non-judgemental.
- Depth interview: 2 people, directive to semi-structure to non-directive, 1h30 to 2h, in home or in facility, recorded, 30 people max, online bulletin.
- Observation: careful finding of facts, behaviours in a given situation and their recording
Advantages and limitations
- Gather detailed information
- Adaptive
- Flexible
- Communicate brand proposition
- Reduce customer churn
- Rigor is required
- Small sample size and representativeness
- Possibility of bias
Quantitative Research
- systematic investigation by gathering quantifiable data and performing statistical, mathematical, or computitional techniques.
- RESULTS = logical, statistical and unbiased.
- COLLECTION = structured, larger sample
Objectives
- Find patterns and averages
- Make predictions
- Test causal relationships
- Generalize results
- Predict the future
Characteristics
- Structured tools
- Large sample size
- Close-ended questions
- Prior studies
- Quantitative data (numbers)
- Generalization of results
- One idea = One question
- Pre-tested
Types
- (Systematic) observation: identify behavior in a natural setting, fill in a grid
- Census: interviewing the whole population, most reliable, too expensive
- Surveys, polls: most widely used, representative sample, questionnaire
- PanelsCollect regularly, provide history and stability, large amounts of data sold to subscribers
Advantages
- Collect reliable data
- Replication
- Direct comparison of results
- Large samples
- Hypothesis testing
- Eliminate bias
Disadvantages
- Superficiality
- Narrow focus
- Structural bias
- Sampling bias

Last updated on